Documentation
Libraries
Related
Documentation
Libraries
Related
This binding has been deprecated - please see the most recent release notes for more information.
In this tutorial you will prepare your development environment for use with the Python bindings for Gestureworks Core. While no code will be written in this tutorial, the steps performed here will prepare your environment for subsequent Gestureworks Core Python tutorials. For this tutorial you will need the Gestureworks Core multitouch framework; a free trial is available.
Download the code for all of the Python & Kivy multitouch tutorials here: tutorials_python_kivy.zip
The various bindings included with Gestureworks Core allow a developer to create multitouch applications using their preferred language and framework, and are essentially mini-APIs providing an interface to the functions exported by the native Gestureworks Core library (GestureWorksCore.dll). Source code for each of the bindings is included so that you may extend or modify them as you like, as well as providing a blueprint for creating bindings for other languages or frameworks.

The Python bindings for Gestureworks Core can be used by any Python project. The source code for the Python bindings is provided for portability and extensibility, but can be used quite effectively as-is in most situations.
![]()
Kivy already has built in multitouch support so why would we integrate it with Gestureworks? Kivy’s gesture recognition is great for basic prototyping or getting a feel for what it’s like to develop using multitouch. However, its true power lies in the simplicity of it’s rendering capabilities. It makes it easy to show the power and versatility of Gestureworks without getting bogged down in rendering graphics and drawing shapes.
Using Gestureworks allows us to utilize a much broader set of gestures. Leveraging GML, we can create a much more flexible and customizable user experience. You don’t need to be a programmer to create and modify custom gestures for you needs.
Finally, by separating gesture processing and rendering, debugging, load balancing, and optimization all become much more simple tasks.
Estimated time to completion: 15 minutes
Each of the following software packages must be downloaded and installed prior to continuing with the tutorial.
The Gestureworks Core installer package – GestureWorksCoreSetup.exe – contains the main GestureWorksCore.dll files (the “native” DLLs), various bindings (C++ .NET, Python, etc.), and supporting documentation. Gestureworks Core must be licensed prior to use in any software project.
GestureWorksCore*.dlls
\GestureWorksCore\GestureWorksCore32.dll
\GestureWorksCore\GestureWorksCore64.dll
Python bindings
\GestureWorksCore\bindings\python\gwc_python
Python tutorials
\GestureWorksCore\bindings\python\kivy\tutorials
Assets for the tutorials
\GestureWorksCore\bindings\python\kivy\assets
You will need to install the PyDev Plugin. In Eclipse, select Help → Install New Software
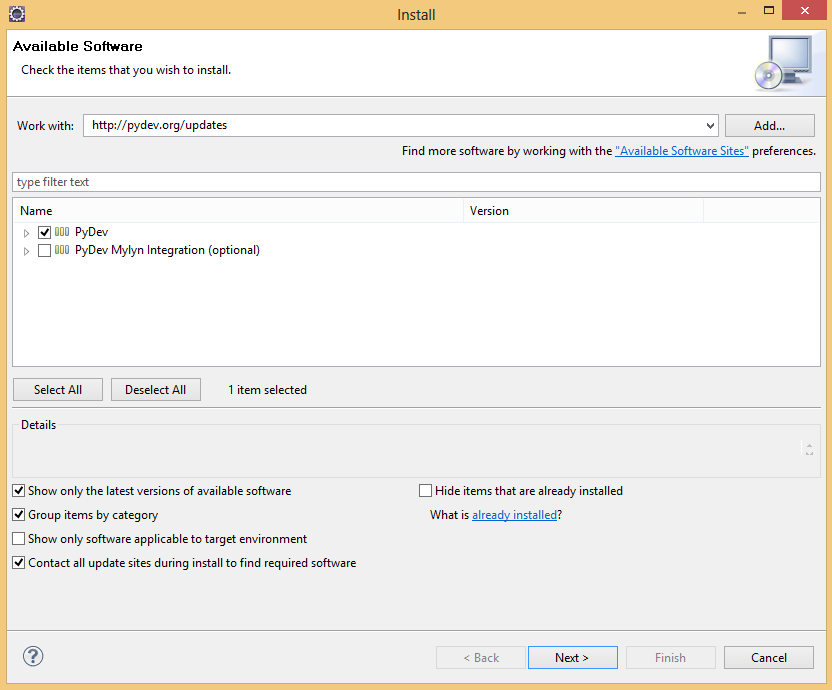
In the Work With field, enter http://pydev.org/updates, check the PyDev package and follow the rest of the instructions. Now that PyDev is installed, we have to configure a Python interpreter to work with Kivy.
Open the Preferences menu by selecting Window → Preferences. Expand the PyDev submenu and select Interpreter - Python. Create a new interpreter and name it something like “Python2.7 - Kivy”, where the path points to the Python interpreter that came with Kivy.
You will also need to add the kivy package folder to the Library.
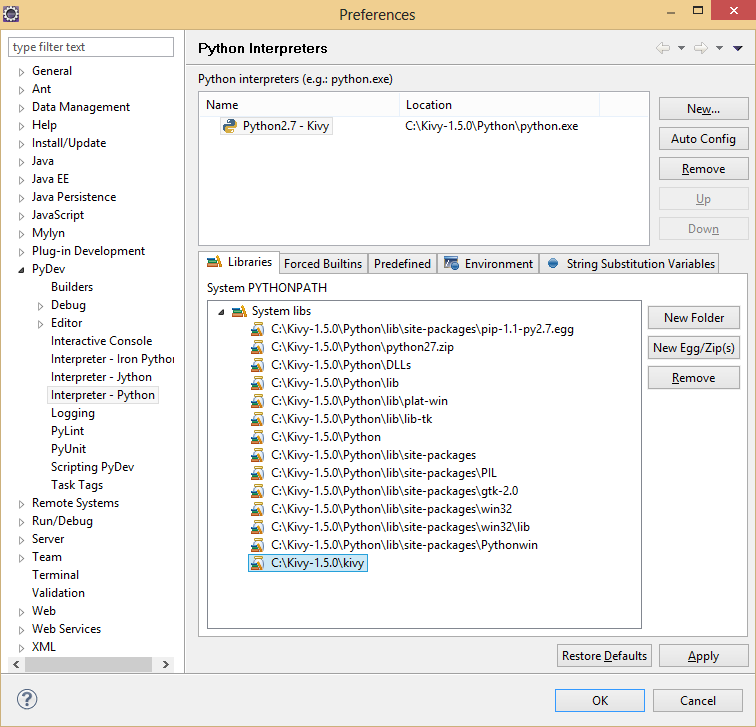
Under the Environment tab, add the following variable mappings:
GST_PLUGIN_PATH = C:\Kivy-1.5.0\gstreamer\lib\gstreamer-0.10 GST_REGISTRY = C:\Kivy-1.5.0\gstreamer\registry.bin PATH = C:\Kivy-1.5.0;C:\Kivy-1.5.0\Python;C:\Kivy-1.5.0\gstreamer\bin;C:\Kivy-1.5.0\MinGW\bin;%PATH%
Kivy provides an easy-to-use framework for developing interactive graphics-based applications using Python. It supplies easy bitmap display and manipulation using the “Scatter” object as well as easily defined timer events that are perfect for use with Gestureworks.
First, create a new Kivy project in Eclipse
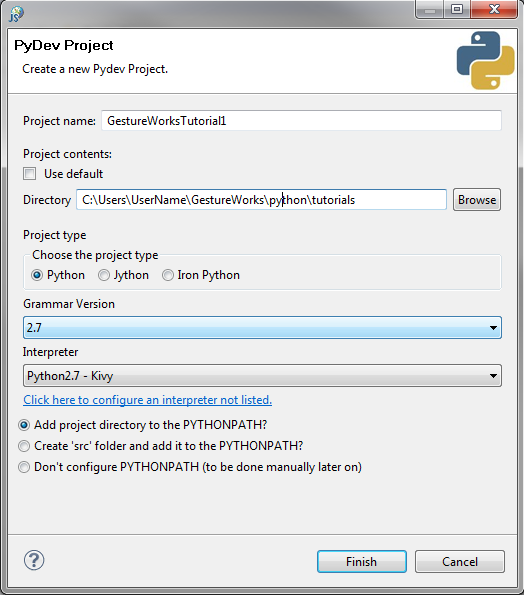
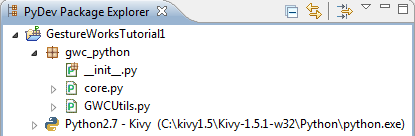
The gwc_python module is the binding layer you will use to communicate with Gestureworks Core.
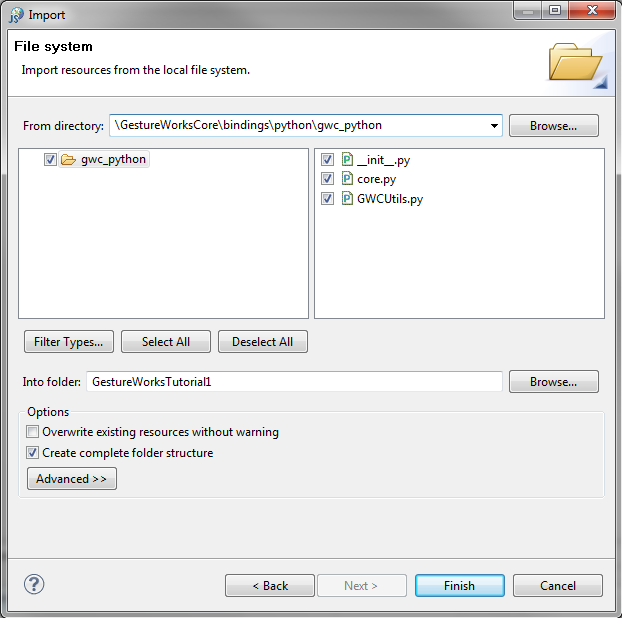
The gwc_python module is now added to the project in Eclipse:
In this tutorial we installed GestureWorks Core, the prerequisites for developing with the GestureWorks Core Python bindings, and created a project that includes the Python binding module. From here we move on to Python & Kivy: Getting Started II (Hello Multitouch) in which we dig into actual source code, initialize GestureWorks Core and work with touch event data.
Next tutorial: Python & Kivy: Getting Started II (Hello Multitouch)